Tankless Water Heater GPM: The Definitive Guide
This is a definitive guide on Tankless Water Heater GPM. Understanding the GPM in a tankless water heater is crucial. It will help you choose a tankless water heater that will meet the requirements of your household’s hot water demands. Here’s what I am going to uncover:
- What is GPM in a tankless water heater?
- What factors affect the GPM in a tankless water heater?
- How do you calculate GPM requirements in tankless water heaters?
- How does the GPM of tankless water heaters compare to traditional ones?
- How do you achieve optimal GPM performance in a tankless water heater?
Table of Contents
- What Is GPM In Tankless Water Heaters?
- What Factors Affect the GPM (Gallons Per Minute) in Tankless Water Heaters?
- How Do You Calculate GPM Requirements For A Tankless Water Heater?
- How Does The Gpm Of Tankless Water Heaters Compare To Traditional Ones?
- How Do You Achieve Optimal GPM Performance In A Tankless Water Heater?
What Is GPM In Tankless Water Heaters?
GPM stands for Gallons Per Minute, also known as Flow Rate. It measures how many gallons of water flow out of your tankless water heater per minute.
From the point of view of a tankless water heater, GPM is a crucial metric that indicates the unit’s capacity to supply hot water on demand. The importance of GPM is directly related to the performance and efficiency of your tankless water heater.
A tankless water heater operates by heating water as it passes through the unit, providing hot water on demand without storing it. The GPM determines how much hot water the unit can deliver each minute. Understanding the GPM is a must for several reasons, including:
- Capacity & Demand: The GPM rating helps you determine if a tankless water heater can meet the hot water demands of your household- like running multiple appliances at a time.
- Avoiding Temperature Fluctuations: Considering GPM in a tankless water heater will help you avoid temperature fluctuations during usage. If the demand for hot water exceeds the GPM capacity of the heater, the resulting decrease in water temperature can affect its overall performance.
- Help You Size The Tankless Unit Properly: Choosing a tankless water heater with a proper GPM rating will ensure that the unit aligns with the hot water demand of your household.
What Factors Affect the GPM (Gallons Per Minute) in Tankless Water Heaters?
Several factors, including water heater capacity, incoming water temperature, and desired hot water temperature, influence the GPM in tankless water heaters. Here is the explanation of those key criteria:
- Water Heater Capacity: The capacity of a tankless water heater is a crucial factor to consider. It represents the amount of water the unit can heat within a specific temperature increase. A higher capacity usually results in a higher Gallons Per Minute (GPM) rate. More capacity in a tankless unit means higher water flow and GPM, enabling the heater to meet the hot water demands of multiple fixtures.
- Incoming Water Temperature: The performance of a tankless water heater in achieving the desired hot water temperature depends on the temperature of the incoming water. In regions with colder climates, your tankless water heater may work harder, potentially reducing the GPM compared to warmer areas.
- Desired Hot Water Temperature: You can adjust the output water temperature on your tankless water heater. However, higher temperature settings may result in a lower GPM, as the unit needs more time to heat the water to the specified temperature.
How Do You Calculate GPM Requirements For A Tankless Water Heater?
Calculating GPM requirements for a tankless water heater is simple. Add the GPM for all major appliances or fixtures you want to use simultaneously. The result you get from the addition represents the GPM requirements for a tankless water heater to meet your household’s needs
Here is the step-by-step guide you can follow to calculate GPM requirements for a tankless water heater:
Identify Peak Hot Water Demand
Peak water usage refers to when you may be running all the major appliances like dishwasher, faucets, and showers at once.
Determine the Flow Rates of Fixtures and Appliances
Find the GPM for each fixture or appliance that uses hot water. Here is the chart of typical flow rate for different appliances and fixtures:
- Sink faucet—1 GPM
- Bathtub—3 GPM
- Shower—2.5 GPM
- Dishwasher—3 GPM
- Clothes washer—3 GPM
Add Up Flow Rates
Sum up the flow rates of those appliances you want to use simultaneously. For example, if you run shower, dishwasher, and sink faucet at a time, the value (using the chart mentioned above) will be 6.5 GPM (2.5+3+1). And this value represents the GPM required to meet your household’s hot water demands.
Consider Temperature Rise
Temperature Rise refers to the difference between the incoming cold water temperature and the desired hot water temperature. To calculate the temperature rise, subtract the desired temperature from the groundwater temperature. Here is the map you can check to find your local US groundwater temperature:
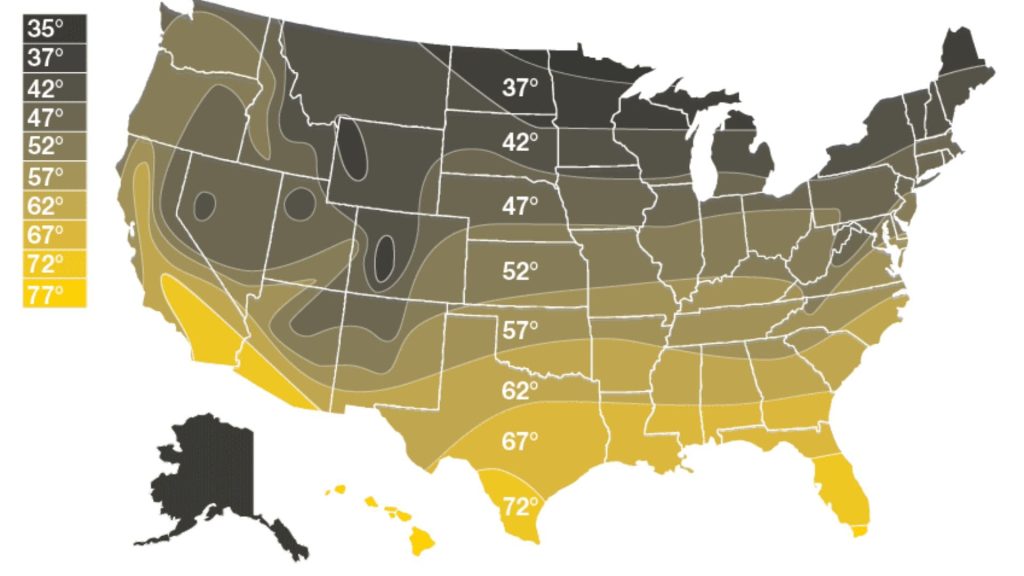
For example, if you live in Florida, your groundwater temperature is 66-97 degrees F. Now, you want the water to be heated around 100–115 degrees F. So, your required Temperature Rise will be 34-18, subtracting the desired hot temperature from the groundwater temperature.
Select A Tankless Water Heater
Check the product details to verify if a tankless water heater will meet your household’s hot water demands while maintaining the temperature rise. Each manufacturer will list the maximum GPM flow rate at different required Temperature Rises. Verify that the tankless unit is sized properly for your specific needs.
How Does The Gpm Of Tankless Water Heaters Compare To Traditional Ones?
Tankless water heaters typically outperform traditional water heaters in terms of GPM (Gallons Per Minute). This is due to the on-demand nature of tankless systems, ensuring a continuous and efficient hot water supply. Unlike traditional water heaters, tankless heaters heat water as it flows through the unit, allowing for a higher GPM during periods of peak demand.
A tankless water heater can deliver 2-12 GPM of hot water based on the model and their fuel types. For example, gas tankless water heaters have higher GPM than electric ones.
On the other hand, the GPM of a traditional tank water heater is lower. A tanked water heater stores a certain amount of water. Besides, the standby heat loss of storage water heaters affects the GPM. These reasons lead to a lower GPM during peak usage.
You can calculate the GPM of a tank water heater by dividing the recovery time by the capacity of the tank. If you have a 50-gallon tank water heater and it takes one hour to recover, then the GPM is 1.2.
How Do You Achieve Optimal GPM Performance In A Tankless Water Heater?
Consider the following tips to gain optimal GPM performance in a tankless water heater:
- Verify that the tankless water heater is sized properly for your household’s hot water demands. An undersized tankless water heater may struggle to provide the desired GPM during peak usage.
- Adjust the temperature setting according to your preferences. If you set the temperature to a higher setting, it may reduce the overall GPM output.
- Perform routine maintenance workflow to let the unit operate more efficiently. It will also contribute to boosting GPM performance.
- Don’t forget to install a water softener if your water contains minerals buildup. It will prevent scale formation in the unit, promoting consistent GPM over time.
- Install the tankless water heater by a professional. A proper installation of the unit increases the efficiency and overall GPM performance.
GPM in a tankless water heater is a metric that indicates how gallons of water flow out of a tankless unit. The GPM rating will help you choose the appropriate tankless water heater for your household’s needs. I uncovered everything you need to know about GPM and how it influences selecting a tankless water heater. So, bookmark this guide or share it with your friends to help them choose a tankless water heater.
Discover More Water Heater Basics In The Water Heater Guide Category.

Sohel Rana is an expert writer (Of course, the owner and founder of this blog) on plumbing, HVAC, and appliance repair & troubleshooting. Since 2020, he has written on these specific topics, though his writing journey began in 2018.






![Types of Water Heater [Complete Guide]](https://lildutchuncle.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/10/Types-of-Water-Heater-Complete-Guide-768x384.webp)
![Rheem Power Vent Water Heater Reset [5 Simple Steps]](https://lildutchuncle.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/09/Rheem-Power-Vent-Water-Heater-Reset--768x384.webp)
