A water heater is not a single device but a combination of different working parts. Each part works simultaneously to operate the unit. If you know how each part of the water heater works, you can easily determine a water heater problem. Apart from this, you can get the right part for replacement. This article on Parts of Water Heaters will describe different types of water heaters and how the components of each water heater work.
Table of Contents
- Common Parts of Water Heaters
- Gas Water Heater Parts
- Electric Water Heater Parts
- Tankless Water Heater Parts
Common Parts of Water Heaters
Here are the common parts you can find on conventional storage water heaters either powered by gas or electric.
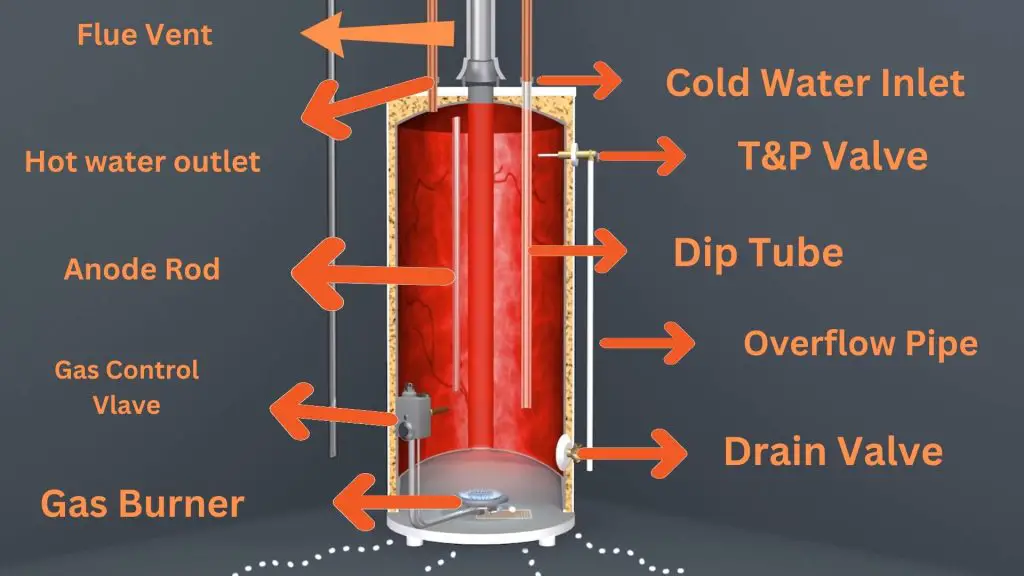
Tank
It doesn’t matter what type of water heater (electric or gas) you have- the tank is the largest part of the unit where heated water is stored until you need it. The water heater tank is made of steel with a glass lining to prevent corrosion.
Dip Tube
A water heater dip tube is an extended plastic tube that runs from the cold water inlet nearly to the bottom of the water heater tank. The function of this tube is to direct cold water from the top to the bottom of the tank, where water can be heated.
Overflow or Discharge Pipe
An overflow or discharge is a piece of copper or flex line that releases excess water when the T&P relief valve opens. This pipe runs from the T&P Relief Valve on the tank’s exterior. When the pressure inside the tank gets excessive, the pressure relief valve opens to escape the pressure through the discharge pipe.
Anode Rod
An anode rod is a metal rod that runs through the length of the tank’s interior. It’s actually a steel wire wrapped in aluminum, magnesium, or zinc. It sacrifices itself and absorbs the minerals and impurities coming with water. As a result, the anode rod gets corroded instead of corroding the tank, which prolongs the tank’s lifespan.
T&P Relief Valve
Temperature and Pressure Relief Valve is a safety device on a water heater. As the name suggests, the pressure relief valve will release excessive pressure buildup to protect your water heater from exploding. When the temperature inside the water gets too high, this component lets the excess pressure escape through the discharge pipe. You can locate the T&P relief valve on the top of the overflow or discharge pipe.
Drain Valve
A water heater drain valve is a small valve at the bottom of the unit. It gives you the control of draining the water from the tank. The key function of this valve is to drain water, which is essential to perform routine maintenance or replacement workflow.
Cold Water Inlet
The cold water inlet lets the cold water enter the water heater when open. You can shut off the water supply by closing the attached valve during repair or maintenance workflows.
Hot Water Outlet
The hot water outlet is the spot on your water heater where heated water exits the tank and flows into your plumbing system. Without it, there’d be no hot showers or warm baths.
Gas Water Heater Parts
Let’s describe how each part of the gas water heater works:

Flue Baffle
The flue baffle helps improve the efficiency and safety of the water heater’s combustion process. It regulates the flow of combustion gasses produced by the burner within the water heater. Then, the flue baffle directs those toxic gasses through the flue or vent pipe to ensure safe exit of the combustion gasses.
Draft Hood or Draft Diverter
You can find the draft hood on the top of a standard atmospheric gas water heater. It’s made of aluminum or mixed metals. The draft hood has a circular shape and three legs, which gives it support and security to set on the top of the unit.
The draft hood helps to regulate the draft or airflow within the venting system of a water heater. It features a series of fins or plates that help to guide the flue and create separation between the hot combustion gas and the surrounding air.
Blower or Fan Assembly
On a power vent water heater, you can see a blower or fan assembly on the top of the unit. The fan assembly provides mechanical assistance for the power vent water heater to expel combustion gasses.
The blower or fan assembly creates a draft or airflow within the power vent water heater. It draws air into the combustion chamber and mixes air with the fuel to produce heat. After combustion, the blower helps expel the combustion gasses, like carbon dioxide, outside the home through the vent pipe.
For proper functioning, the blower requires a separate electric power source from the rest of the gas water heater.
Gas Burner
The gas burner is a crucial part of a water heater that heats up the water inside the tank. It works by burning natural gas or propane to produce heat, which is then transferred to the water in the tank. This process is what makes the water hot and ready for use in your home.
Gas Control Valve
The gas control valve is a device that helps you start and stop the gas supply to the gas burner. It is usually located at the bottom of the water heater. The gas valve has a thermostat that monitors the temperature of the water in the tank.
When the temperature drops below the desired level, the gas control valve opens up and allows gas to flow to the burner. This starts the heating process of the water. When the water temperature reaches the desired level, the gas valve stops the gas supply to maintain the set temperature.
Pilot Assembly
The pilot assembly on a water heater is responsible for igniting the gas burner to heat water inside the tank. It consists of a small, continuously burning flame that serves as a source of ignition for the main burner. When the unit is in standby mode, the pilot light remains lit, ready to ignite the gas burner when hot water is needed.
Thermocouple
A thermocouple is a safety device that is a part of the pilot assembly in a gas water heater. Its job is to sense the presence of a flame. If the flame goes out, the thermocouple cools down quickly, and this causes a drop in the electric voltage it generates. This drop in voltage signals the gas control valve to shut off the gas supply to the burner. This is to prevent any gas buildup, which could be dangerous.
Flammable Vapor Sensor
Modern gas water heaters are equipped with a special safety device called a flammable vapor sensor. It is designed to detect any flammable vapors that might be present near the water heater, like gasoline or paint thinner. If the sensor detects these materials, it will automatically shut off the gas supply to the burner and turn off the unit. This is an important safety feature that helps prevent accidents and keeps you and your home safe.
Flue or Vent Pipe
The flue or vent pipe is a part of the water heater that helps to release the harmful gasses produced during the heating process safely outside. It is usually located at the top of the water heater and can either be a vertical or horizontal pipe that goes outside. This way, the combustion gasses are released into the air outside, and the water heater can work safely and efficiently.
Electric Water Heater Parts
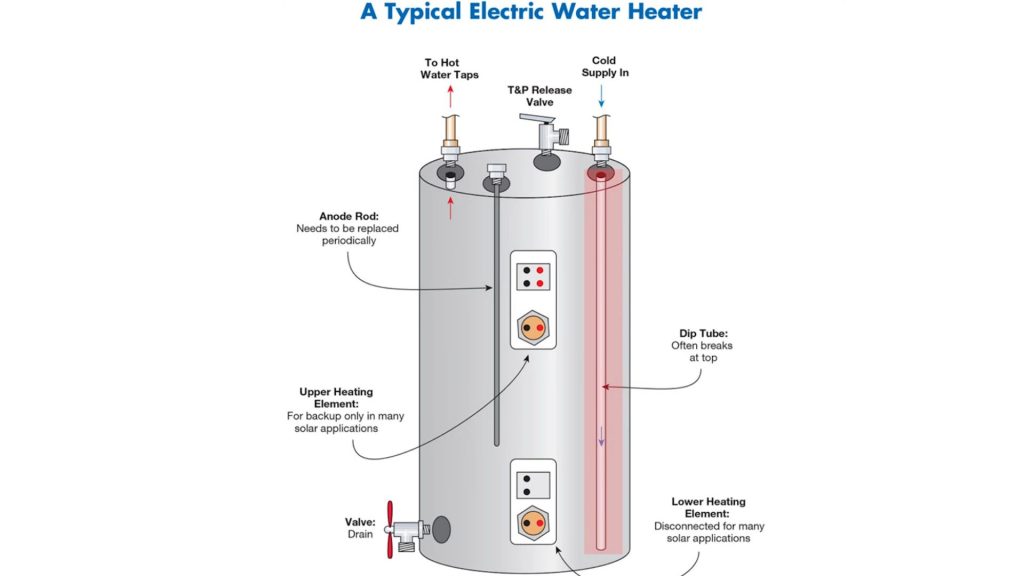
Here are some unique parts of electric storage water and how they work:
Electrical Supply/Breaker
An electric water heater requires an electric power source to operate the unit. Electric supply for electric water heaters refers to the electrical wiring and connection point that delivers power to the unit. It typically involves connecting the water heater to the electrical panel or junction box in the home using appropriate wiring and connectors. On the other hand, the circuit breaker works as a safety device. It protects the water heater’s circuit from overloading or electrical faults.
Heating Element
A heating element is a metal rod responsible for heating the water. The metallic rod converts electrical energy into heat. When electricity flows through the heating element, it encounters resistance and generates heat. You can locate the heating elements inside the water heater tank, immersed in the water.
They are usually positioned near the bottom or side of the tank to heat the entire volume of water efficiently. Most electric water heaters have two heating elements. The bottom heating element heats the water first and the second one will heat the water when the hot water demand is excessive.
Thermostat
Every electric water heater has a thermostat to monitor the temperature inside the tank. Actually, it’s a temperature control switch in a water heater that activates or deactivates the heating element to maintain the desired temperature setting.
Insulation
The insulation of a water heater plays an important role in keeping the water warm for a longer period of time. It acts as a blanket and prevents the heat from escaping out of the tank. By keeping the water warm for a longer time, it helps the water heater work more efficiently, reducing energy usage and the cost of running it.
Tankless Water Heater Parts
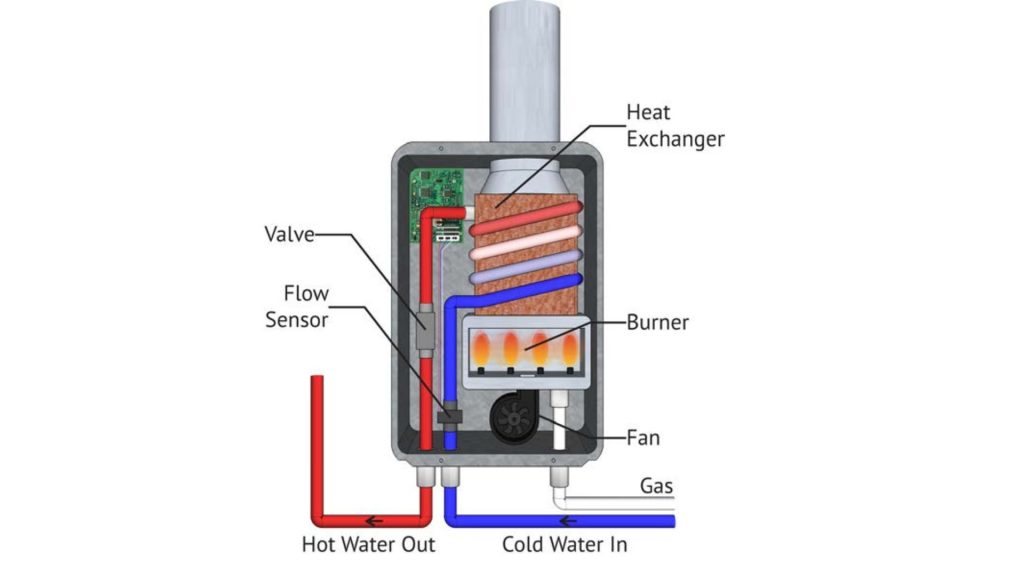
Tankless water heaters are the new edition in the water heating industry. Many homeowners are switching from storage to tankless units because of the benefits of tankless water heater. That’s why it’s essential to learn about the function of each component of the tankless water heater. This chapter will break down the functionality of each part.
Heat Exchanger
The tankless water heater has a very important part called the heat exchanger, often called as the core of the unit. This part moves heat from the burner to the water. When cold water goes into the water heater, it goes through the heat exchanger, which heats up the water by using heat from the flames.
Flow Sensor
A flow sensor on a tankless water heater detects or monitors the flow rate of water passing through the unit. When the sensor detects the flow rate, it sends a signal to the control board, indicating that hot water is required. Based on the signal, the control board prompts the unit to activate and start heating.
Control Panel
The control panel of a tankless water heater is like a control center for the unit. It’s where you can manage the water heater’s performance. The control panel usually comes with buttons, dials, or a touchscreen display that allows you to adjust the temperature, flow rate, and other settings.
Gas Valve or Electric Power Supply
To heat the water in your home, your water heater requires a specific energy source. Gas-powered models typically require a gas supply line to function, while electric models need to be connected to an electrical source. This distinction is important to keep in mind when choosing the right water heater for your needs. A gas tankless water heater has a gas valve to let you open or close the gas supply to the unit. On the other hand, an electric tankless water heater has a power cord that needs to be plugged into an outlet.
Safety Devices
Tankless water heaters have built-in safety measures for worry-free operation. They include temperature sensors to avoid overheating, pressure relief valves to prevent explosions, and flame failure sensors to stop gas flow if the flame goes out. These features ensure a safe and steady supply of hot water for your home.
Venting System
Gas-powered tankless water heaters require a venting system to safely release harmful combustion gasses outside. This crucial safety feature safeguards the health and safety of occupants by preventing indoor air pollution.

Sohel Rana is an expert writer (Of course, the owner and founder of this blog) on plumbing, HVAC, and appliance repair & troubleshooting. Since 2020, he has written on these specific topics, though his writing journey began in 2018.





